This 500-Year-Old Tale Resurfaces After the Discovery of Lost Ancient Shipwrecks from the Ming Dynasty
This discovery of two marine vessels in the South China Sea by researchers has sparked conversation around the fabled Ming dynasty.
Now, archaeologists are studying the well-preserved relics as they could unveil valuable insight into the marine capabilities of China’s most prosperous ancient dynasties.
The Ming Dynasty
The Ming dynasty, believed to be one of the most powerful dynasties that brought a period of stability to China, lasted from 1368 to 1644.

Source: Wikimedia Commons
During the late medieval period, scholars studied this dynasty as it proved to have impressive trading capabilities and preservation, which showed how the dynasty influenced the world beyond its borders.
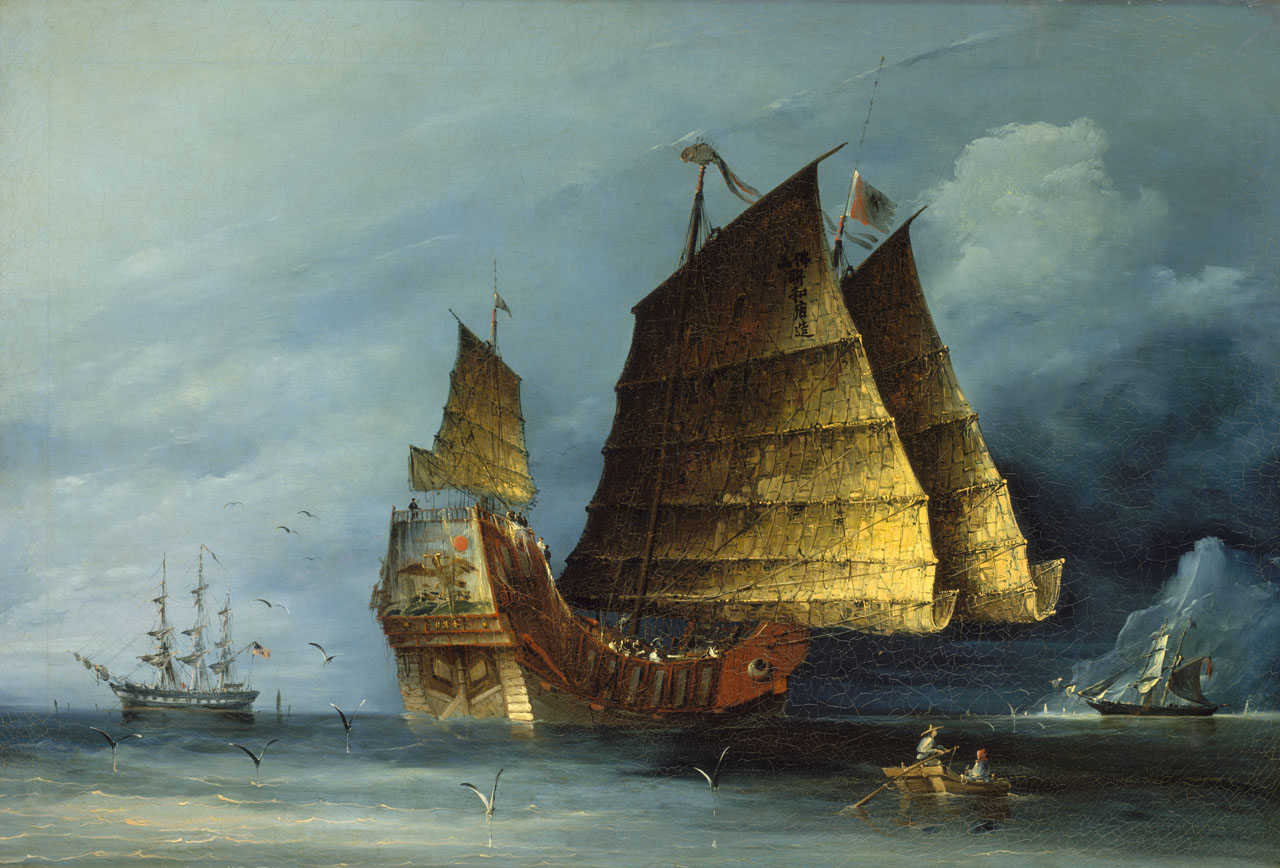
Impressive Voyages That Opened Up Trade
One point of interest in the Ming dynasty was the impressive voyages and trading systems established. These voyages took Chinese merchants further than they had ever traveled before.

Source: National Maritime Museum, Greenwich
Establishing water routes allowed the Ming dynasty to extend its dominance in trade, facilitating the export and import of goods previously unseen.
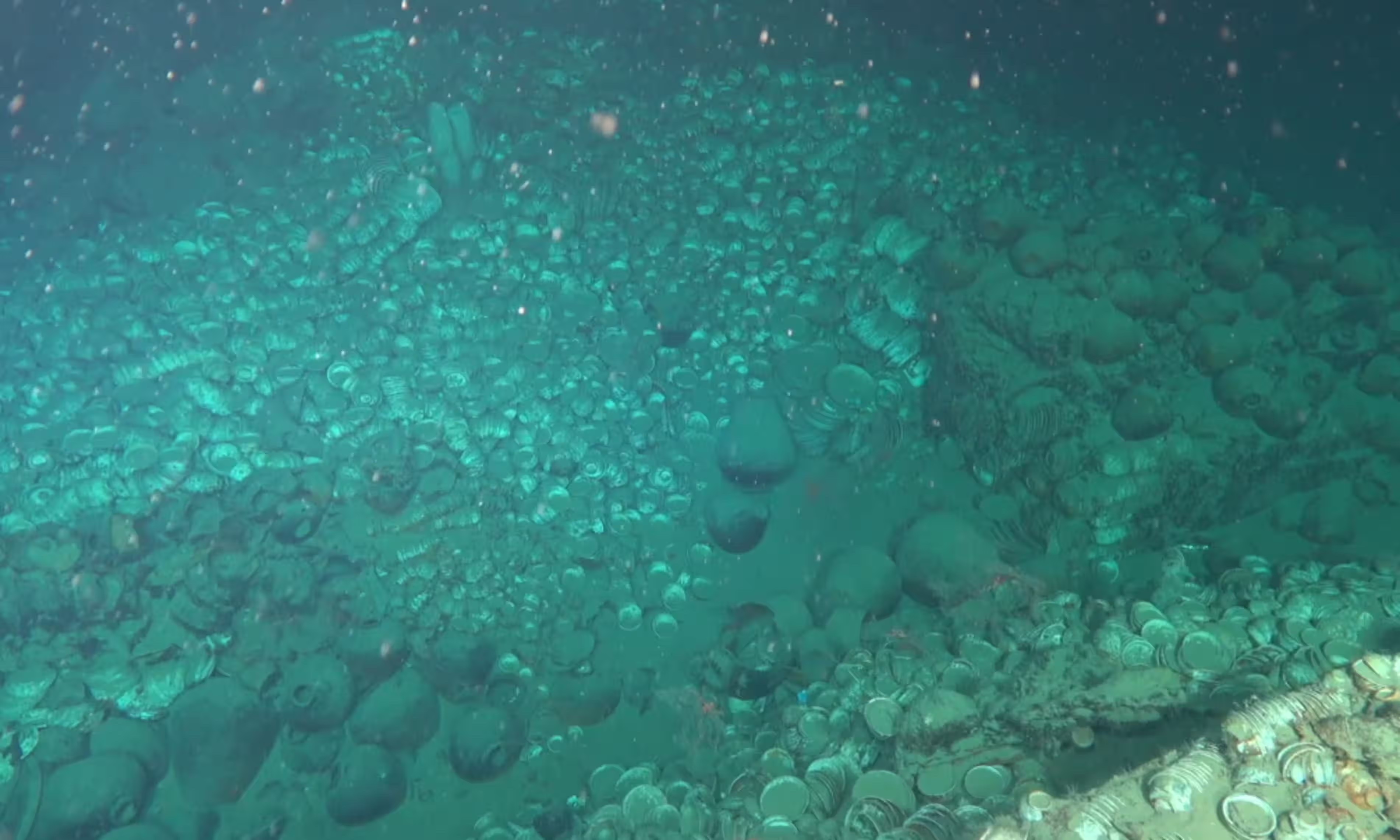
The Discovery of Ancient Ships
The discovery of two ancient ships in October astonished researchers who had been scouring the sea floor for notable artifacts.

Source: Freepik
China’s State Administration of Cultural Heritage announced that this discovery marked the first instance of ancient ships, which sailed and returned to the same sea, being discovered in the country.
A Historical Find
According to the Chinese government, archaeologists will begin excavating the site with deep-sea excavation equipment. The excavation process could take up to a year.

Source: State Administration of Cultural Heritage Government of Hainan province
“The well-preserved relics are of high historical, scientific, and artistic value. It may be a world-class archaeological discovery in the deep sea,” said Yan Yalin, the director of archaeology for the cultural heritage agency, in a statement.
The Lucky Discovery
The ships were located about 1,500 meters deep underwater on the northwest slope of the sea, approximately 10 nautical miles apart.

Source: Harvey Clements/Pexels
Discovering the ships was fortunate in itself, but researchers also found that they were “relatively well preserved, with a large number of cultural relics,” according to a spokesperson quoted by The Guardian.
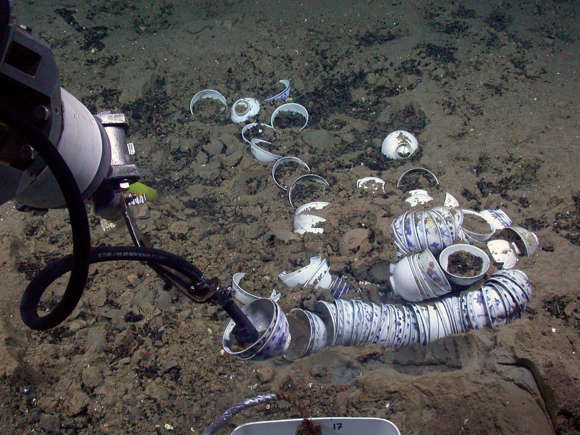
The Exports of the Ships
According to researchers who discovered the ships, one of the ancient ships appeared to have exploited porcelain while the other imported wood. After initial inspections, the researchers announced that the ships contained Ming-era artifacts.

Source: benjancewicz/X
This discovery could help Chinese archaeologists further their understanding of the Ming dynasty’s trading routes.
Uncovering History
According to Yan, the discovery holds significant importance in unraveling ancient China’s international trading connections.

Source: adiprayogo liemena/Pexels
“The remarkably preserved artifacts possess considerable historical, scientific, and artistic significance… and represent a significant advancement in the study of Chinese maritime trade, navigation, and porcelain history,” as reported by The Vintage News.
Dating the Ships
Initial dating methods, which include inspecting the DNA of delicate waterlogged wood, provided researchers with data suggesting that one vessel dates to the Hongzhi era (1488 to 1505).

Source: Public Domain/Wikimedia Commons
The data from the other ship dates it to the Zhengde era of the Ming dynasty (1506 to 1526). This ship was packed with historically significant artifacts.
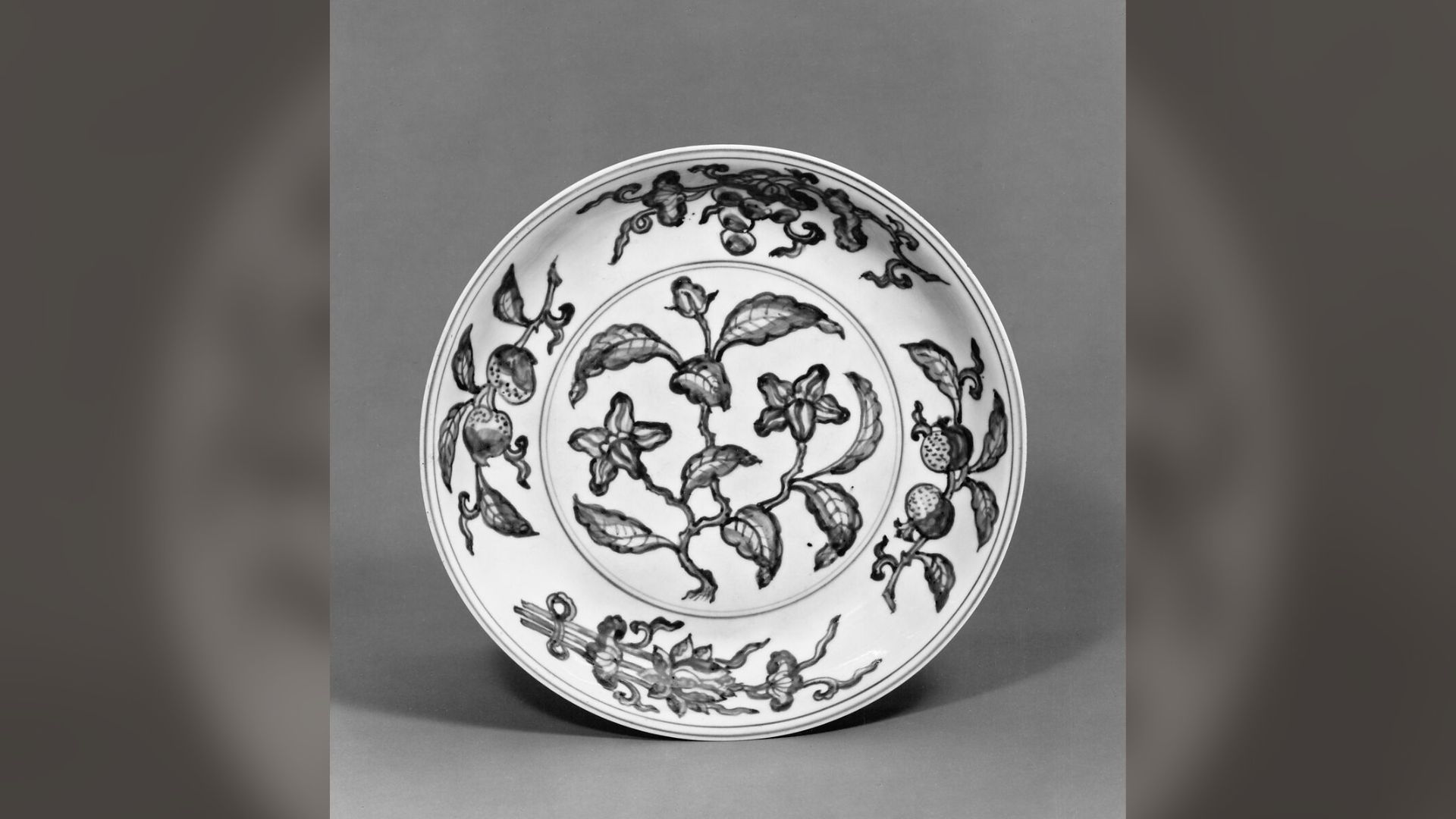
The Riches of One Ship
The ship, dating back to the Zhengde era, was estimated to carry over 100,000 items made from porcelain.

Source: Public Domain/The Met
These items ranged from jars to plates to bowls, all intricately decorated with Ming-era artwork.
Unearthing Another Silk Road
Archaeologists identified the location where the ships were found as a vital trade route on the South China Sea. Researchers have started to theorize what role this maritime highway could have played in the Ming dynasty’s impressive era of trade.
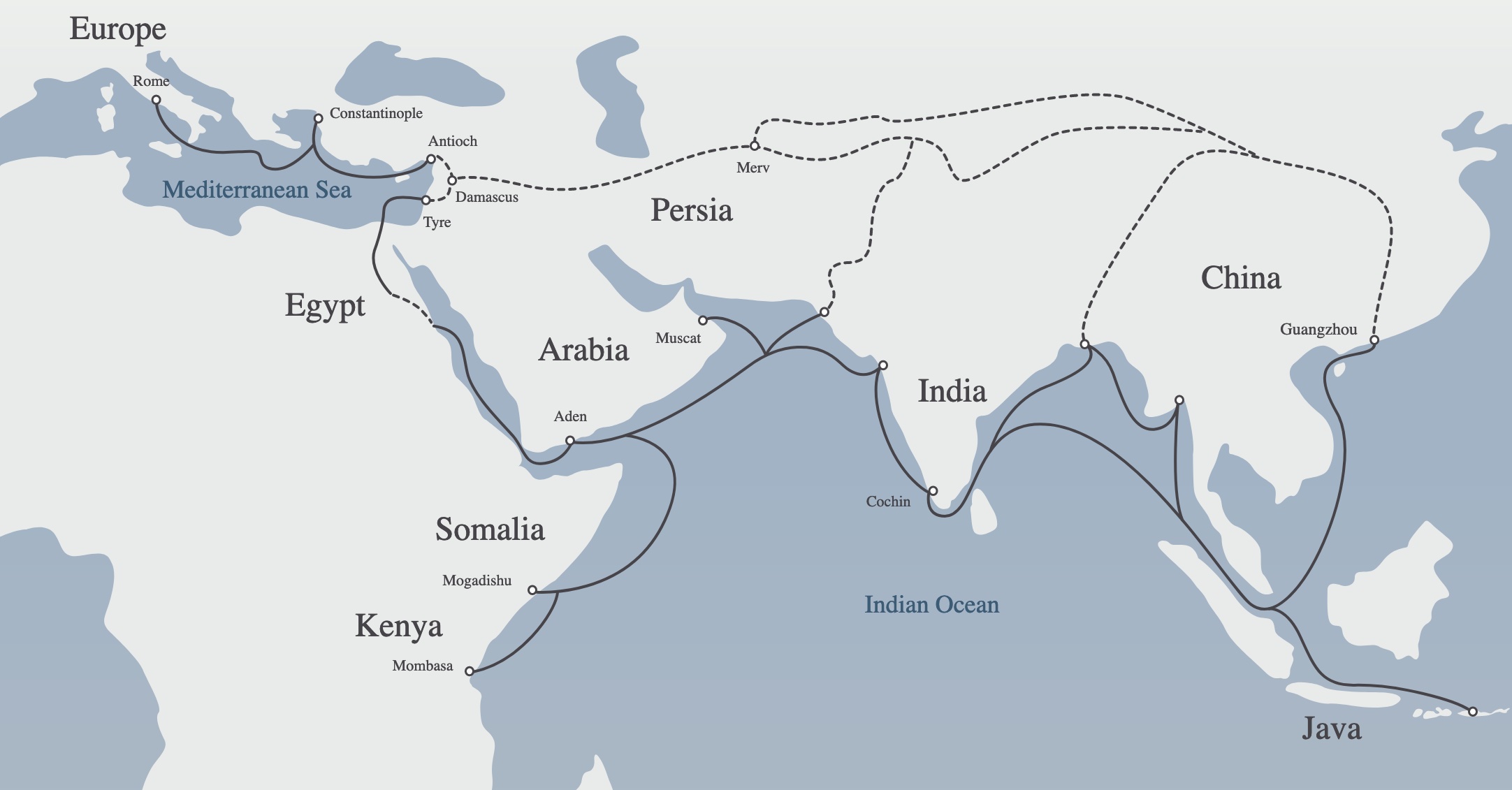
Source: Wikimedia Commons
According to Tani Wei, director of the Chinese National Center for Archaeology, “It helps us study the maritime Silk Road’s reciprocal flow.”
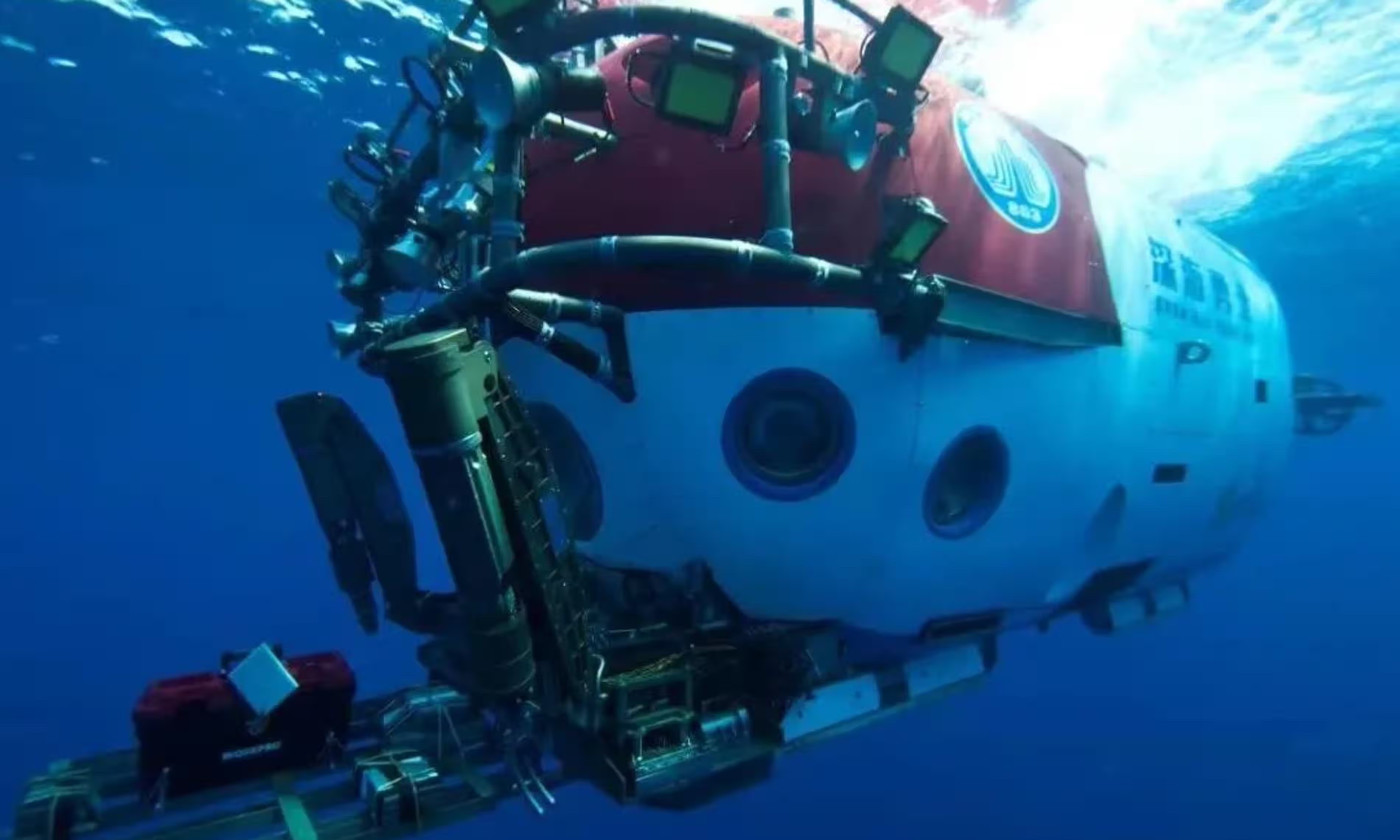
Research Begins
The National Center of Archaeology and the Institute of Deep-sea Science and Engineering will help Chinese researchers and archaeologists using the Shenhai Youngshi, a submersible vessel, to further explore the remains of the ships.

Source: State Administration of Cultural Heritage Government of Hainan province
“We first need to figure out the condition of the shipwrecks, and then we can draft plans for archaeological excavation and conservation,” Song Jianzhong, a researcher at the National Centre for Archaeology, told The Guardian.
Advances in Underwater Archaeology Technology
Modern underwater archaeology has seen significant advancements with the integration of technology. In the discovery of the Ming shipwrecks, sophisticated 3D sonar imaging and robotic divers were crucial (via the Chinese Academy of Science).

Source: Joseph Barrientos/Unsplash
These technologies allowed researchers to navigate and document the deep-sea environment meticulously, ensuring precise mapping and safe artifact retrieval.
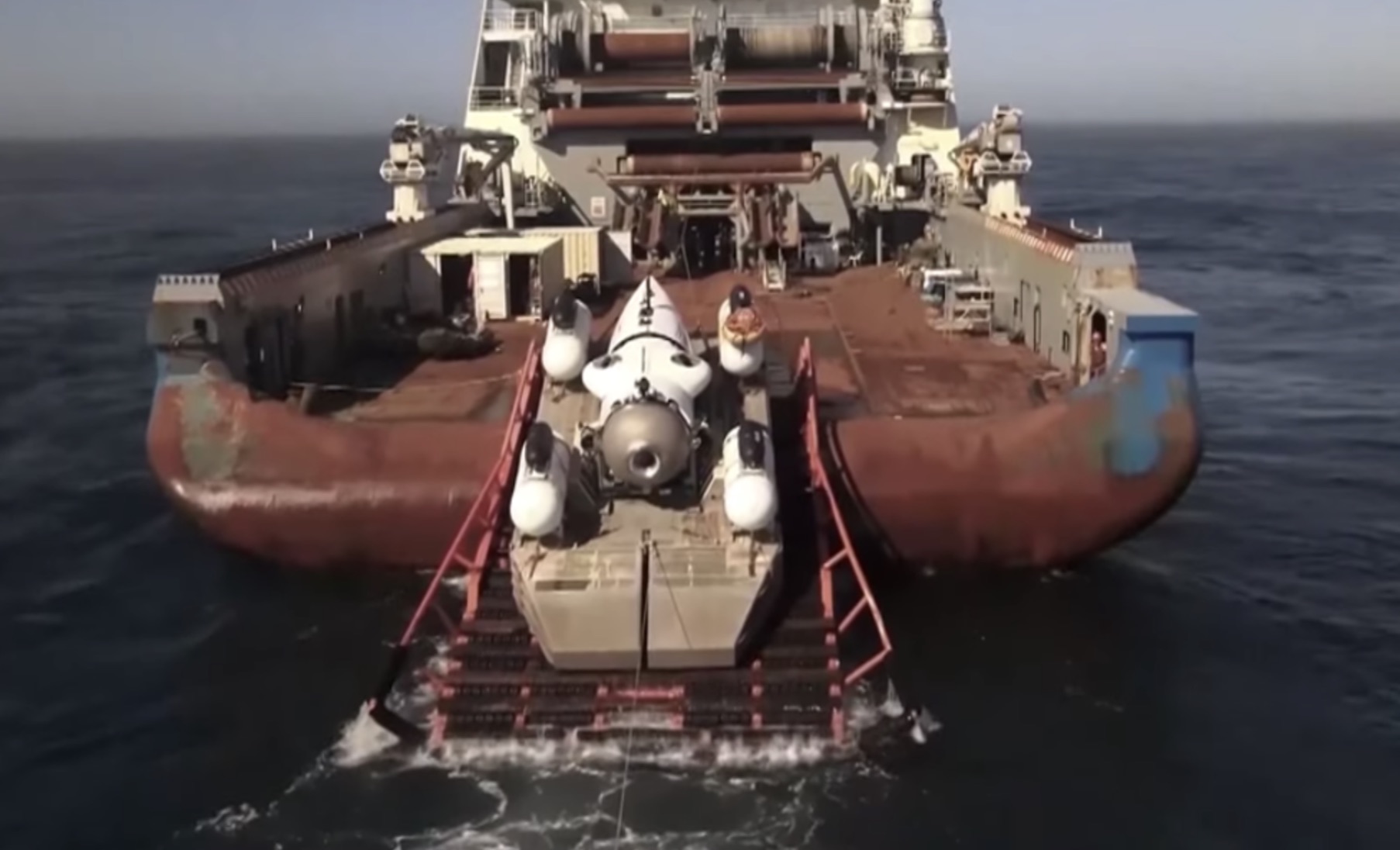
Remote Operated Vehicles (ROVs) in Action
Remote Operated Vehicles (ROVs) played a pivotal role in exploring the Ming dynasty shipwrecks.

Source: On Demand News/YouTube
These underwater robots, equipped with high-definition cameras and mechanical arms, can operate at depths unreachable by human divers (via NOAA).
Sonar Technology and Mapping the Sea Floor
Sonar technology has revolutionized the way archaeologists locate and study submerged artifacts.
![Sonar image of the Soviet Navy minesweeper T-297, formerly the Latvian Virsaitis, which was shipwrecked on 3 December 1941 in the Gulf of Finland[1]](https://images.crowndaily.com/2024/04/9e95573e-sonar.jpg)
Source: Tuukritööde OÜ/Wikipedia
By emitting sound waves and analyzing their echoes, sonar creates detailed maps of the sea floor, revealing hidden shipwrecks and artifacts (via NOAA). This method was instrumental in pinpointing the location of the ancient Ming vessels, laying the groundwork for their exploration.
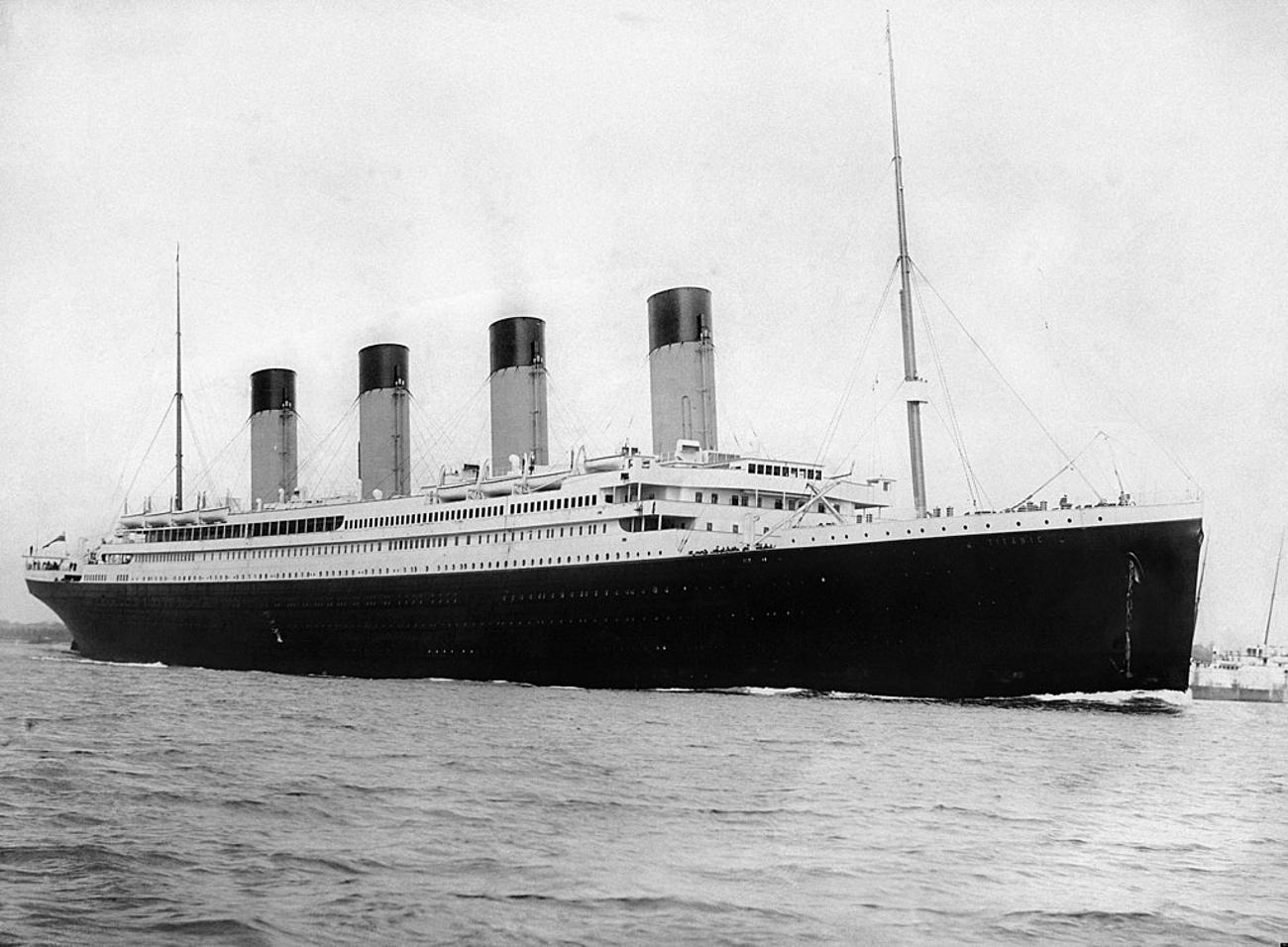
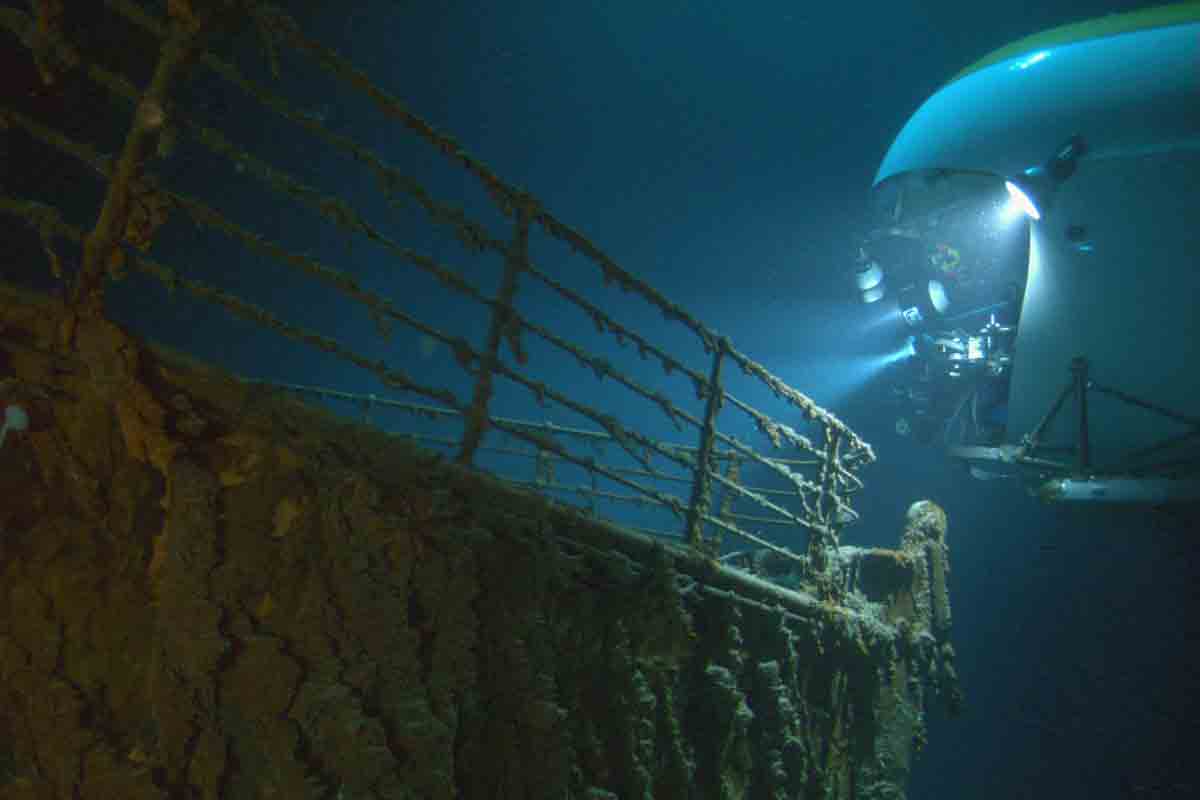
Comparison with Titanic's Discovery
The discovery of the Ming shipwrecks can be compared with the exploration of the Titanic.

Source: Wikipedia
While both employed remote technology and robotic aids, the Ming exploration benefited from more advanced sonar and imaging technologies, demonstrating how far marine archaeology has advanced in just a few decades.
Impact of Saltwater on Underwater Artifacts
According to a Texas A&M University study, saltwater poses a significant challenge to preserving underwater artifacts, as it accelerates corrosion and decay. The Ming shipwrecks’ artifacts are subject to these conditions, making their conservation a delicate task.

Source: Alamy
Specialized baths and other techniques are required to stabilize and restore these items once they are brought to the surface.
Techniques in Preserving Delicate Artifacts
Methods such as desalination baths, which remove salt deposits, and vacuum freeze-drying, which stabilizes waterlogged wood, are crucial (via Car Wreck Divers).

Source: Titanic Museum
These processes help ensure that the artifacts can be studied and displayed without further deterioration.
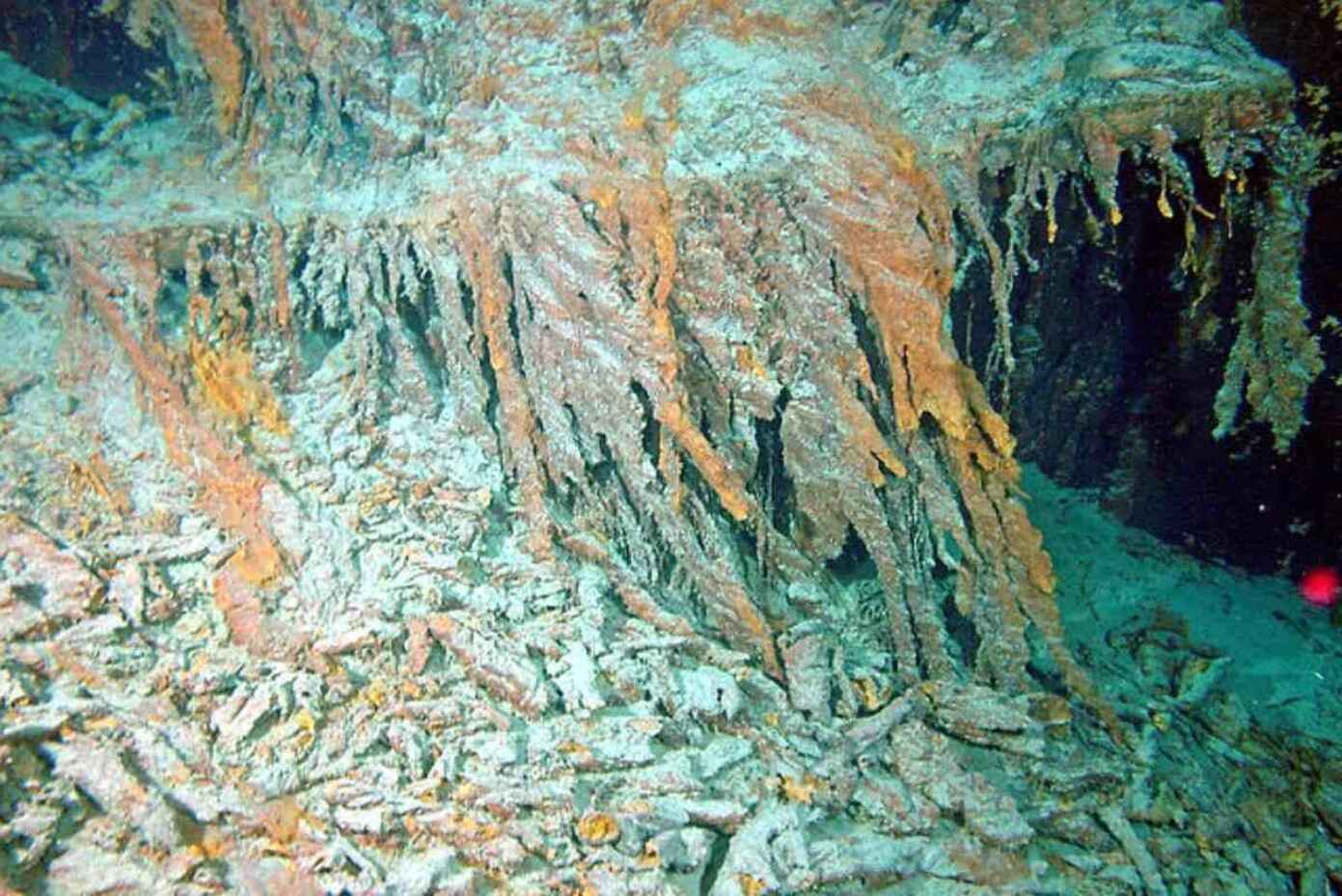
Archaeological Excavation Process
The process of excavating underwater sites like the Ming shipwrecks is also methodical and complex. It begins with a detailed survey using sonar and photographic documentation, followed by the careful retrieval of artifacts using specialized equipment.

Source: Lori Johnston, RMS Titanic Expedition 2003, NOAA-OE/ Wikimedia Commons
Each step is meticulously planned to avoid damaging the delicate historical items.
DNA Analysis of Waterlogged Wood
Per scientist Lisa Briggs, DNA analysis has become a vital tool in underwater archaeology, particularly for dating and conserving artifacts.

Source: Warren Umoh/Unsplash
By analyzing the DNA of waterlogged wood from the Ming shipwrecks, researchers can determine the age of the ships and better understand the materials used in their construction, which provides insights into Ming-era shipbuilding techniques.
The Legal Framework of Underwater Cultural Heritage
The protection of underwater cultural heritage is governed by international treaties and national laws.

Source: Freepik
The UNESCO 2001 Convention on the Protection of the Underwater Cultural Heritage sets standards for preserving historical artifacts found in international waters and facilitates cooperation among countries in their archaeological efforts.
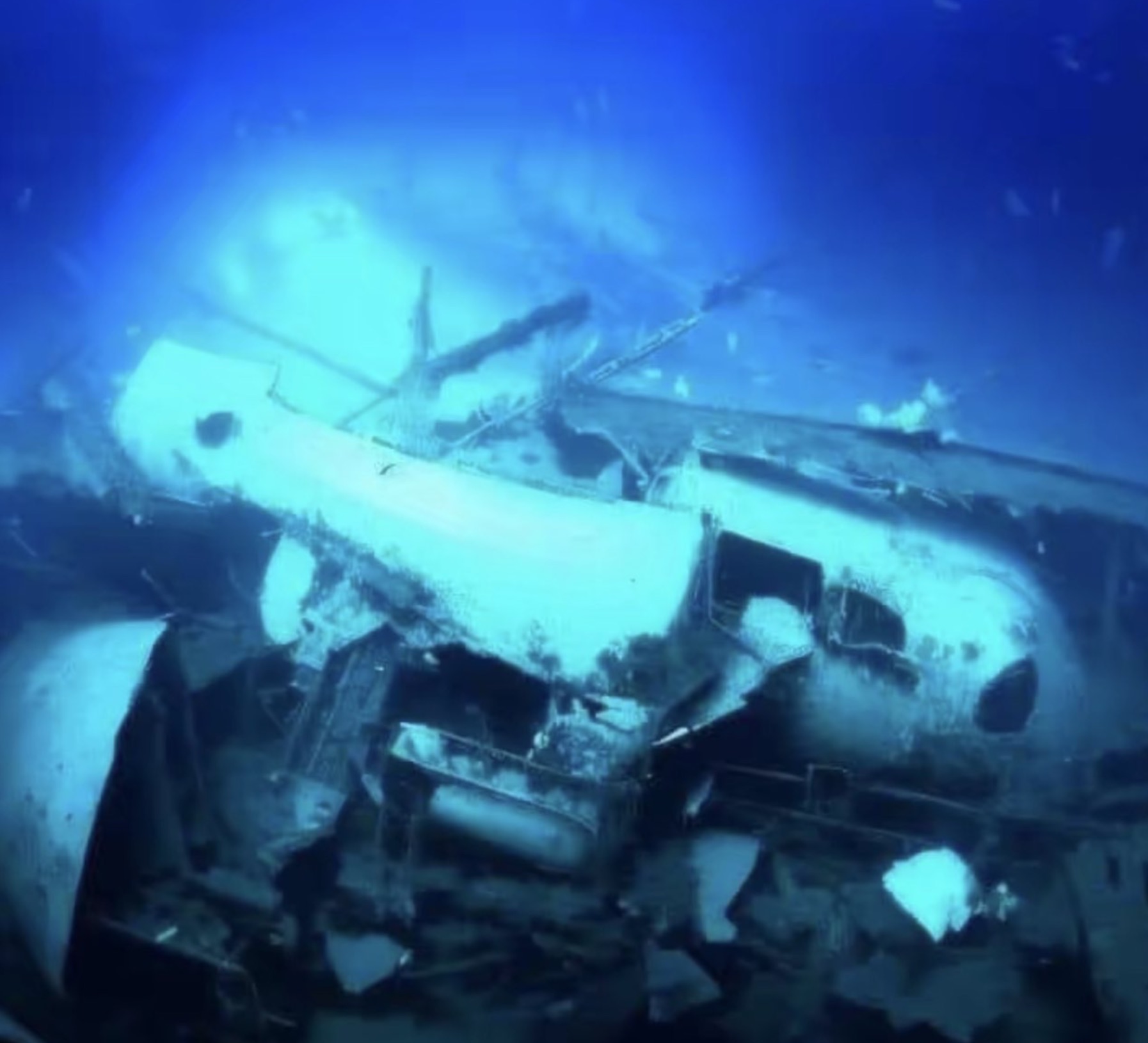
Ethical Considerations in Underwater Archaeology
Ethical considerations in underwater archaeology include the decision to remove artifacts from their resting places.

Source: @GlockSwitchGTA/X
Researchers must balance the scientific value of artifacts with the respect due to historical sites, often seen as underwater cultural landscapes or maritime gravesites.
The Future of Protecting Underwater Cultural Sites
The future of protecting underwater cultural sites likely involves more advanced technologies and increased international cooperation.

Source: Adventures of Maldives/Unsplash
Innovations in imaging and remote exploration could further minimize the need for disruptive excavation methods, preserving the integrity of submerged sites while still revealing their historical secrets.
Enhancing Public Engagement and Education
Public engagement and education are also important in the field of underwater archaeology. By using immersive technologies such as virtual reality (VR), museums and educational institutions could potentially offer virtual tours of the Ming Dynasty shipwrecks, allowing people worldwide to explore these ancient relics from their own homes.

Source: ThisIsEngineering/Pexels
This approach not only makes the discoveries accessible but also raises awareness about the importance of preserving underwater cultural heritage.
